Krita, Kṛta, Krīta, Kṛtā: 28 definitions
Introduction:
Krita means something in Buddhism, Pali, Hinduism, Sanskrit, Jainism, Prakrit, the history of ancient India, Marathi, Hindi. If you want to know the exact meaning, history, etymology or English translation of this term then check out the descriptions on this page. Add your comment or reference to a book if you want to contribute to this summary article.
The Sanskrit terms Kṛta and Kṛtā can be transliterated into English as Krta or Krita, using the IAST transliteration scheme (?).
In Hinduism
Purana and Itihasa (epic history)
Source: Wisdom Library: Bhagavata PuranaKṛta (जय):—Son of Jaya (son of Sañjaya, who was the son of Prati). He had a son named Haryabala. (see Bhāgavata Purāṇa 9.17.16)
Source: archive.org: Puranic Encyclopedia1) Kṛta (कृत).—A King of Janaka’s dynasty. He was the son of Vijaya and father of Śunaka. (Bhāgavata, 9th Skandha). Kṛta had seven beautiful daughters who, because of a sense of non-attachment and renunciation, forsook their father’s home for the cremation ground even while they were mere children. They lay down there declaring that they had left their bodies as food for the birds; and birds and wild beasts ate up their beautiful bodies. Because of this life of renunciation, they attained salvation. (Kathāsaritsāgara, Madanamañjukālambaka, Taraṅga 2).
2) Kṛta (कृत).—A Viśvadeva (Universal Deva). (Anuśāsana Parva, Chapter 91, Verse 31).
Source: Cologne Digital Sanskrit Dictionaries: The Purana Index1a) Kṛta (कृत).—The son of Jaya and father of Haryavana.*
- * Bhāgavata-purāṇa IX. 17. 17.
1b) A son of Vasudeva and Rohiṇī.*
- * Bhāgavata-purāṇa IX. 24. 46.
1c) A son of Sannati (m.p.); a pupil of Hiraṇyanābha; in yoga imparted twenty-four saṃhitas to his disciples;1 chief among the Sāmayas by arranging sāma veda in 24 parts.2 Father of Ugrāyudha.3
- 1) Bhāgavata-purāṇa XII. 6. 80; Brahmāṇḍa-purāṇa II. 35. 49 and 55; Vāyu-purāṇa 99. 189-90; Viṣṇu-purāṇa III. 16. 7.
- 2) Matsya-purāṇa 49. 75-6.
- 3) Viṣṇu-purāṇa IV. 19. 50-3.
1d) An Yakṣa and a son of Devayāni.*
- * Brahmāṇḍa-purāṇa III. 7. 130.
1e) Married Śrutadevī; father of Sugrīva.*
- * Matsya-purāṇa 46. 5.
1f) A son of Viśvāmitra.*
- * Vāyu-purāṇa 91. 96.
1g) A son of Kanaka.*
- * Vāyu-purāṇa 94. 8.
1h) A son of Hṛdika.*
- * Vāyu-purāṇa 96. 139.
1i) A son of Cyavana.*
- * Vāyu-purāṇa 99. 219.
1j) A son of Vijaya; father of Haryadhana.*
- * Viṣṇu-purāṇa IV. 9. 26-7.
1k) Sets in when the sun, moon, Tiṣya and Bṛhaspati (Planet Jupiter) are in the same mansion.*
- * Viṣṇu-purāṇa IV. 24. 102.

The Purana (पुराण, purāṇas) refers to Sanskrit literature preserving ancient India’s vast cultural history, including historical legends, religious ceremonies, various arts and sciences. The eighteen mahapuranas total over 400,000 shlokas (metrical couplets) and date to at least several centuries BCE.
Natyashastra (theatrics and dramaturgy)
Source: Wisdom Library: Nāṭya-śāstraKṛta (कृत) is another name (synonym) of bhāva, referring to “psychological states” (eg. permanent, involuntary, transitory), according to the Nāṭyaśāstra chapter 7.

Natyashastra (नाट्यशास्त्र, nāṭyaśāstra) refers to both the ancient Indian tradition (shastra) of performing arts, (natya—theatrics, drama, dance, music), as well as the name of a Sanskrit work dealing with these subjects. It also teaches the rules for composing Dramatic plays (nataka), construction and performance of Theater, and Poetic works (kavya).
Dharmashastra (religious law)
Source: Shodhganga: The Vyavaharadhyaya of the YajnavalkyasmritiKrīta (क्रीत) refers to one of the twelve types of sons (putra) defined in the Vyavahārādhyāya of the Yājñavalkyasmṛti verse 2.128-132.—If a son is sold by both mother and father, or by either of them, then the son is called Krīta or a son bought. The Mitākṣarā states that he should be sold not being the eldest or only son, in the time of distress and to him, belonging to the same class.

Dharmashastra (धर्मशास्त्र, dharmaśāstra) contains the instructions (shastra) regarding religious conduct of livelihood (dharma), ceremonies, jurisprudence (study of law) and more. It is categorized as smriti, an important and authoritative selection of books dealing with the Hindu lifestyle.
Vyakarana (Sanskrit grammar)
Source: Wikisource: A dictionary of Sanskrit grammarKṛta (कृत).—(१) a term used by ancient grammarians in the sense of 'past tense';(2) effected, done. The word is mostly used in this sense in grammar.works;e.g. किं तेन कृतं स्यात् (kiṃ tena kṛtaṃ syāt) ; नानुबन्धकृतमनेकात्त्वम् (nānubandhakṛtamanekāttvam) Par. Śek.Pari. 6.

Vyakarana (व्याकरण, vyākaraṇa) refers to Sanskrit grammar and represents one of the six additional sciences (vedanga) to be studied along with the Vedas. Vyakarana concerns itself with the rules of Sanskrit grammar and linguistic analysis in order to establish the correct context of words and sentences.
Kavya (poetry)
Source: Wisdom Library: KathāsaritsāgaraKṛta (कृत) is the name of an ancient king, as mentioned in the Kathāsaritsāgara, chapter 28. Accordingly, “long ago, there were born in succession to a certain king named Kṛta seven very beautiful princesses, and even while they were still youthful they abandoned, in disgust with life, the house of their father, and went to the cemetery...”.
The story of Kṛta was narrated to king Kaliṅgadatta by a religious preacher in order to demonstrate that “a wise man should do what is beneficial to other beings, by abstaining from selfish aspirations even so far as to sacrifice his own body, in order that he may obtain perfect insight”.
The Kathāsaritsāgara (‘ocean of streams of story’), mentioning Kṛta, is a famous Sanskrit epic story revolving around prince Naravāhanadatta and his quest to become the emperor of the vidyādharas (celestial beings). The work is said to have been an adaptation of Guṇāḍhya’s Bṛhatkathā consisting of 100,000 verses, which in turn is part of a larger work containing 700,000 verses.

Kavya (काव्य, kavya) refers to Sanskrit poetry, a popular ancient Indian tradition of literature. There have been many Sanskrit poets over the ages, hailing from ancient India and beyond. This topic includes mahakavya, or ‘epic poetry’ and natya, or ‘dramatic poetry’.
Ayurveda (science of life)
Source: gurumukhi.ru: Ayurveda glossary of termsKṛta (कृत):—Material is fried by using ghee or oil by addition of pungents, mustard, asa foetida & turmeric etc.

Āyurveda (आयुर्वेद, ayurveda) is a branch of Indian science dealing with medicine, herbalism, taxology, anatomy, surgery, alchemy and related topics. Traditional practice of Āyurveda in ancient India dates back to at least the first millenium BC. Literature is commonly written in Sanskrit using various poetic metres.
Shaktism (Shakta philosophy)
Source: Google Books: ManthanabhairavatantramKṛta (कृत) or Kṛtayuga refers to the age associated with Oḍḍiyāna, one of the sacred seats (pīṭha), according to the Manthānabhairavatantra, a vast sprawling work that belongs to a corpus of Tantric texts concerned with the worship of the goddess Kubjikā.—The Kumārikākhaṇḍa displays most of the many new developments that took place after the revelation of the Kubjikāmatatantra including those concerning the sacred seats. [...] Although the seats are the same five described in the Kubjikāmatatantra and its expansions, their contents [i.e., the Kṛta-yuga] and the beings who inhabit them are quite different.

Shakta (शाक्त, śākta) or Shaktism (śāktism) represents a tradition of Hinduism where the Goddess (Devi) is revered and worshipped. Shakta literature includes a range of scriptures, including various Agamas and Tantras, although its roots may be traced back to the Vedas.
Ganitashastra (Mathematics and Algebra)
Source: archive.org: Hindu MathematicsKṛta (कृत) represents the number 4 (four) in the “word-numeral system” (bhūtasaṃkhyā), which was used in Sanskrit texts dealing with astronomy, mathematics, metrics, as well as in the dates of inscriptions and manuscripts in ancient Indian literature.—A system of expressing numbers by means of words arranged as in the place-value notation was developed and perfected in India in the early centuries of the Christian era. In this system the numerals [e.g., 4—kṛta] are expressed by names of things, beings or concepts, which, naturally or in accordance with the teaching of the Śāstras, connote numbers.
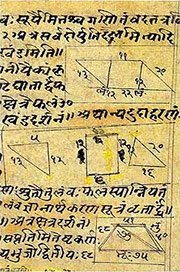
Ganitashastra (शिल्पशास्त्र, gaṇitaśāstra) refers to the ancient Indian science of mathematics, algebra, number theory, arithmetic, etc. Closely allied with astronomy, both were commonly taught and studied in universities, even since the 1st millennium BCE. Ganita-shastra also includes ritualistic math-books such as the Shulba-sutras.
In Buddhism
Mahayana (major branch of Buddhism)
Source: academia.edu: A Study and Translation of the GaganagañjaparipṛcchāKṛta (कृत) (Cf. Akṛta) refers to “(that which is) created”, according to the Gaganagañjaparipṛcchā: the eighth chapter of the Mahāsaṃnipāta (a collection of Mahāyāna Buddhist Sūtras).—Accordingly, “Then, the Lord went on to speak these verses: ‘[...] (44) Action (karma), which is neither created (akṛta) nor imagined (acintya) and which is thus not discriminated (akalpita), does not have any form (rūpa) or color (varṇa) such as red, blue, and yellow. [...]’”.

Mahayana (महायान, mahāyāna) is a major branch of Buddhism focusing on the path of a Bodhisattva (spiritual aspirants/ enlightened beings). Extant literature is vast and primarely composed in the Sanskrit language. There are many sūtras of which some of the earliest are the various Prajñāpāramitā sūtras.
General definition (in Buddhism)
Source: Wisdom Library: Dharma-samgrahaKṛta (कृत) or Kṛtayuga refers to the “accomplished age ” and represents the first of the “four ages” (yuga) as defined in the Dharma-saṃgraha (section 88). The Dharma-samgraha (Dharmasangraha) is an extensive glossary of Buddhist technical terms in Sanskrit (e.g., kṛta). The work is attributed to Nagarjuna who lived around the 2nd century A.D.
In Jainism
General definition (in Jainism)
Source: Wisdom Library: JainismKṛta (कृत) refers to “done by self” and it is one of the factors making up the 108 kinds of adhikaraṇa (‘substratum’) of the living beings (jīva). This substratum (instruments of inflow) represents the foundation or the basis of an entity.
Kṛta is a Sanskrit technical term defined in the Tattvārthasūtra (ancient authorative Jain scripture) from the 2nd century, which contains aphorisms dealing with philosophy and the nature of reality.
Source: Encyclopedia of Jainism: Tattvartha Sutra 6: Influx of karmasKṛta (कृत).—What is meant by ‘doing’ (kṛta)? To perform the activity is called “doing’.

Jainism is an Indian religion of Dharma whose doctrine revolves around harmlessness (ahimsa) towards every living being. The two major branches (Digambara and Svetambara) of Jainism stimulate self-control (or, shramana, ‘self-reliance’) and spiritual development through a path of peace for the soul to progess to the ultimate goal.
India history and geography
Source: Cologne Digital Sanskrit Dictionaries: Indian Epigraphical GlossaryKṛta.—(EI 12, 14, 23; BL; CII 3), literally ‘accomplished’. i. e. ‘completed’; used in earlier records in connection with the era later associated with Vikramāditya. Often spelt krita, possibly standing for krīta meaning ‘purschased’, which was a name sometimes applied to certain foreign rulers of North-Western Bhāratavarṣa (Ep. Ind., Vol. XXXIII, p. 152). (IE 7-1-2), ‘four’. (CII 1), ‘arranged for’, ‘made arrangements for’. (EI 23), fruit, booty, reward. (Sel. Ins., p. 202), ‘engraved’. (Ep. Ind., Vol. XXXIV, p. 41, verse 13), written, drafted or composed. Note: kṛta is defined in the “Indian epigraphical glossary” as it can be found on ancient inscriptions commonly written in Sanskrit, Prakrit or Dravidian languages.

The history of India traces the identification of countries, villages, towns and other regions of India, as well as mythology, zoology, royal dynasties, rulers, tribes, local festivities and traditions and regional languages. Ancient India enjoyed religious freedom and encourages the path of Dharma, a concept common to Buddhism, Hinduism, and Jainism.
Languages of India and abroad
Marathi-English dictionary
Source: DDSA: The Molesworth Marathi and English Dictionarykṛta (कृत).—n S The first of the four ages of the world, satyayuga.
--- OR ---
kṛta (कृत).—p (S) Done, made, performed. Elegantly prefixed in comp. implying That has done or made. Ex. kṛtabhōjana That has dined or made his meal; kṛtavivāha That has married; kṛtāparādha Guilty or faulty; kṛtasnāna, kṛtābhyaṅga, kṛtapraṇāma, kṛtanigraha, kṛtātithya, kṛtānugraha, kṛtaprasāda, kṛtaprasthāna, kṛtayajña. Others more valuable or less obvious are inserted and explained in order.
--- OR ---
krīta (क्रीत).—p S Bought. 2 Sold. 3 Used as s m, being abridged from krītaputra, A purchased son. This is one of the twelve heirs.
Source: DDSA: The Aryabhusan school dictionary, Marathi-Englishkṛta (कृत).—n The 1st of the 4 ages of the world. p Done.
--- OR ---
krīta (क्रीत).—p Sold. Bought.
Marathi is an Indo-European language having over 70 million native speakers people in (predominantly) Maharashtra India. Marathi, like many other Indo-Aryan languages, evolved from early forms of Prakrit, which itself is a subset of Sanskrit, one of the most ancient languages of the world.
Sanskrit dictionary
Source: DDSA: The practical Sanskrit-English dictionaryKṛta (कृत).—p. p. [kṛ-kta]
1) Done, performed, made, effected accomplished, manufactured &c.; (p. p. of kṛ 8. U. q. v.) ते करान् संप्रयच्छन्तु सुवर्णं च कृताकृतम् (te karān saṃprayacchantu suvarṇaṃ ca kṛtākṛtam) Mahābhārata (Bombay) 3.255.17; दिव्याः प्रसन्ना विविधाः सुराः कृतसुरा अपि (divyāḥ prasannā vividhāḥ surāḥ kṛtasurā api) Rām.5.11.22; natural and manufactured wines.
2) Wounded, hurt; सिद्ध्येत ते कृतमनोभवधर्षितायाः (siddhyeta te kṛtamanobhavadharṣitāyāḥ) Bhāgavata 3.23.11.
3) Acquired, bought (a kind of son); Mahābhārata (Bombay) 13.49.4.
4) Cultivated; अकृतं च कृतात्क्षेत्राद् गौरजाविकमेव च (akṛtaṃ ca kṛtātkṣetrād gaurajāvikameva ca) Manusmṛti 1.114.
5) Appointed (as a duty); सोऽपि यत्नेन संरक्ष्यो धर्मो राजकृतश्च यः (so'pi yatnena saṃrakṣyo dharmo rājakṛtaśca yaḥ) Y.2.186.
6) Relating to, referring to; पतनीयकृते क्षेपे (patanīyakṛte kṣepe) Y.2.21.
-tam 1 Work, deed, action; कृतं न वेत्ति (kṛtaṃ na vetti) Pañcatantra (Bombay) 1.424; ungrateful; Manusmṛti 7.197.
2) Service, benefit.
3) Consequence, result.
4) Aim, object.
5) Name of that side of a die which is marked with four points; this is lucky; cf. Vāj.3.18.
6) Name of the first of the four Yugas of the world extending over 1728 years of men (see Manusmṛti 1.69 and Kull. thereon).
7) The number '4'.
8) A stake at a game.
9) Prize or booty gained in a battle.
1) An offering.
11) Magic sorcery.
--- OR ---
Krīta (क्रीत).—p. p. Bought; see क्री (krī).
-taḥ One of the twelve kinds of sons recognised in Hindu Law; a son purchased from his natural parents; Manusmṛti 9.16; क्रीतश्च ताभ्यां वि- क्रीतः (krītaśca tābhyāṃ vi- krītaḥ) Y.2.131; तव क्रीतसुतोऽस्मीति वाचिकेन व्यजिज्ञपत् (tava krītasuto'smīti vācikena vyajijñapat) Śiva. B.31.32.
-tam A bargain.
Source: Cologne Digital Sanskrit Dictionaries: Edgerton Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit DictionaryKṛta (कृत).—(-kṛta) (1) in dṛṣṭi-kṛta, q.v., lit. perhaps (what has) become…, or (subst.) matter of…; seems = (dṛṣṭi-)gata; (2) according to Senart = kṛtya (q.v. 2) as equivalent of adj. formation or gen. case-form, in Mahāvastu ii.274.4 udyānakṛtā āsanā, allegedly les sièges du jardin. But does it not mean quite literally and simply seats made in the park? In Mahāvastu ii.245.5 read with mss. karaṇḍe mālakṛto, in the garland- maker's basket (stem māla-kṛt).
Source: Cologne Digital Sanskrit Dictionaries: Shabda-Sagara Sanskrit-English DictionaryKṛta (कृत).—mfn.
(-taḥ-tā-taṃ) 1. Done, made, performed. 2. Injured, hurt. 3. Fit, proper. n.
(-taṃ) 1. The first of the four ages of the world, the Satyayug. 2. Fruit, consequence. adv. 1. Enough, sufficient. 2. Enough, completely finished. 3. Enough, have done, no more. E. kṛ to do, to injure, &c. affix kta.
--- OR ---
Krīta (क्रीत).—mfn.
(-taḥ-tā-taṃ) Bought, purchased. m.
(-taḥ) A son, one of the twelve kinds acknowledged by the ancient Hindu law; he who is purchased from his natural parents. E. kṛ to buy, affix kta.
Source: Cologne Digital Sanskrit Dictionaries: Cappeller Sanskrit-English DictionaryKṛta (कृत).—[adjective] made, done, prepared, arranged, appointed, got; present, ready, fit, proper, good. Often °— having done, doing using, showing, betraying etc. —[neuter] it is done, i.e. shall be done instantly; [with] [instrumental] (±saha) be it done with, i.e. away with, enough of! [neuter] as subst. act, deed, work, [especially] religious work, sacrifice, ceremony, etc.; service, benefit; stake at game; booty in battle; the (lucky) Four-side of the die; the first or golden age. kṛtena because or instead of ([genetive] or —°); kṛte the same. abs. for something.
--- OR ---
Kṛtā (कृता).—[feminine] cleft, abyss.
--- OR ---
Krīta (क्रीत).—[adjective] bought ([especially] a son); [neuter] buying.
Source: Cologne Digital Sanskrit Dictionaries: Monier-Williams Sanskrit-English Dictionary1) Kṛta (कृत):—[from kṛ] 1. kṛta mfn. done, made, accomplished, performed, [Ṛg-veda; Atharva-veda] etc.
2) [v.s. ...] prepared, made ready, [ib.]
3) [v.s. ...] obtained, gained, acquired, placed at hand, [Atharva-veda iii, 24, 5]
4) [v.s. ...] well done, proper, good, [Śatapatha-brāhmaṇa iv]
5) [v.s. ...] cultivated, [Manu-smṛti x, 114]
6) [v.s. ...] appointed (as a duty), [Yājñavalkya ii, 186]
7) [v.s. ...] relating or referring to, [Yājñavalkya ii, 210]
8) [v.s. ...] m. Name of one of the Viśve Devās, [Mahābhārata xiii, 4356]
9) [v.s. ...] of a son of Vasu-deva, [Bhāgavata-purāṇa ix, 24, 45]
10) [v.s. ...] of a son of Saṃnati and pupil of Hiraṇya-nābha, [Harivaṃśa 1080; Bhāgavata-purāṇa xii, 6, 80]
11) [v.s. ...] of a son of Kṛta-ratha and father of Vibudha, [Viṣṇu-purāṇa]
12) [v.s. ...] of a son of Jaya and father of Haryavana, [Bhāgavata-purāṇa ix, 17, 17]
13) [v.s. ...] of a son of Cyavana and father of Upari-cara, [Vāyu-purāṇa]
14) [v.s. ...] n. (with saha or with [instrumental case]) ‘done with’, away with, enough of, no need of, etc. (e.g. kṛtaṃ saṃdehena, away with doubt, [Śakuntalā]; kṛtaṃ parihāsena, enough of joking, [ib.])
15) [v.s. ...] the past tense, [Aitareya-brāhmaṇa v, 1]
16) [v.s. ...] deed, work, action, [Ṛg-veda; Atharva-veda; Śvetāśvatara-upaniṣad; Manu-smṛti] etc.
17) [v.s. ...] service done, kind action, benefit (cf. kṛta-jña and -ghna), [Mahābhārata v, 1692; Pañcatantra]
18) [v.s. ...] magic, sorcery, [Sāma-vidhāna-brāhmaṇa]
19) [v.s. ...] consequence, result, [cf. Lexicographers, esp. such as amarasiṃha, halāyudha, hemacandra, etc.]
20) [v.s. ...] aim, [Vopadeva i, 2]
21) [v.s. ...] stake at a game, [Ṛg-veda; Atharva-veda]
22) [v.s. ...] prize or booty gained in battle, [ib.]
23) [v.s. ...] Name of the die or of the side of a die marked with four points or dots (this is the lucky or winning die), [Vājasaneyi-saṃhitā xxx, 18; Taittirīya-saṃhitā; Śatapatha-brāhmaṇa] etc.
24) [v.s. ...] (also the collective Name of the four dice in opposition to the fifth die called kali [commentator or commentary] on [Vājasaneyi-saṃhitā x, 28])
25) [v.s. ...] (hence) the number ‘four’ [Varāha-mihira’s Bṛhat-saṃhitā; Sūryasiddhānta]
26) [v.s. ...] Name of the first of the four ages of the world (also called satya or ‘the golden age’, comprehending together with the morning and evening dawn 4800 years of men [Manu-smṛti; Mahābhārata; Harivaṃśa] or according to the later conception [Bhāgavata-purāṇa] etc. [commentator or commentary] on [Manu-smṛti i, 69] 4800 years of the gods or 1728000 years of men)
27) [from kṛ] 2. kṛta mfn. injured, killed, [cf. Lexicographers, esp. such as amarasiṃha, halāyudha, hemacandra, etc.] (cf. 2. kīrṇa.)
28) Kṛtā (कृता):—[from kṛt] a f. an abyss, [Ṛg-veda ii, 35, 5.]
29) [v.s. ...] (also) a skin, hide (= kṛti), [Mānava-gṛhya-sūtra]
30) b See √2. kṛt.
31) Krīta (क्रीत):—[from krī] a mfn. bought, purchased, [Śatapatha-brāhmaṇa; Manu-smṛti] etc.
32) [v.s. ...] purchased from his natural parents (as a son; one of the twelve kinds of sons acknowledged by the ancient Hindū law), [Manu-smṛti ix, 160]
33) [v.s. ...] won by ([instrumental case]), [Śakuntalā iii] ([varia lectio])
34) [v.s. ...] ifc. (with the purchase-price; f(ī). ), [Pāṇini 4-1, 50; vi, 2, 151]
35) [v.s. ...] mf(ā or ī)n. (f. also ā), [Siddhānta-kaumudī]
36) [v.s. ...] m. Name of a man, [Maitrāyaṇī-saṃhitā iv, 2, 6]
37) [v.s. ...] m. [plural] a sort of despised caste, [Horace H. Wilson]
38) [v.s. ...] n. a bargain [commentator or commentary] on [Yājñavalkya ii, 6.]
39) b etc. See √krī.
Source: Cologne Digital Sanskrit Dictionaries: Yates Sanskrit-English Dictionary1) Kṛta (कृत):—[(taḥ-tā-taṃ) p.] Done. 1. n. The Satya-yug, the first of the four ages of the world; fruit. adv. Enough.
2) Krīta (क्रीत):—[(taḥ-tā-taṃ) p.] Bought.
Source: DDSA: Paia-sadda-mahannavo; a comprehensive Prakrit Hindi dictionary (S)Kṛta (कृत) in the Sanskrit language is related to the Prakrit words: Kaella, Kaḍa, Kijjaa, Garia.
[Sanskrit to German]
Sanskrit, also spelled संस्कृतम् (saṃskṛtam), is an ancient language of India commonly seen as the grandmother of the Indo-European language family (even English!). Closely allied with Prakrit and Pali, Sanskrit is more exhaustive in both grammar and terms and has the most extensive collection of literature in the world, greatly surpassing its sister-languages Greek and Latin.
Hindi dictionary
Source: DDSA: A practical Hindi-English dictionaryKrīta (क्रीत) [Also spelled krit]:—(a) bought, purchased; —[dāsa] a paid-for slave.
...
Kannada-English dictionary
Source: Alar: Kannada-English corpusKṛta (ಕೃತ):—[adjective] made; done; performed; finished; accomplished.
--- OR ---
Kṛta (ಕೃತ):—
1) [noun] first of the four mythological ages of the world extending over 17,28,000 years, regarded as the age of truth.
2) [noun] a man who has accomplished (his object).
3) [noun] Yama, the God of Death.
4) [noun] a kindly, charitable act or gift; beneficence; benevolence.
5) [noun] an adequate quantity or amount; sufficiency.
6) [noun] a work, deed; an action that is complete.
7) [noun] consequence; result.
8) [noun] an aim; an object.
9) [noun] a stake at a game.
10) [noun] loot taken from the enemy; spoils of war; booty.
11) [noun] ಕೃತಮಱಿ [kritamari] křtamaṛi to remember the help received (from another); to be grateful; to be thankful.
--- OR ---
Krīta (ಕ್ರೀತ):—[adjective] obtained by paying a price; bought; purchased.
--- OR ---
Krīta (ಕ್ರೀತ):—[noun] a boy adopted by a person, by paying money to the parent or parents of the boy.
Kannada is a Dravidian language (as opposed to the Indo-European language family) mainly spoken in the southwestern region of India.
See also (Relevant definitions)
Starts with (+407): Krita-pranta, Krita-upasanna, Kritabahu, Kritabandhu, Kritabashakthika, Kritabhaga, Kritabhajana, Kritabharana, Kritabhava, Kritabhaya, Kritabhisaranavesha, Kritabhisheka, Kritabhiyoga, Kritabhojana, Kritabhumi, Kritabhutamaitra, Kritabhyanujna, Kritabhyasa, Kritabrahman, Kritabuddhi.
Ends with (+831): Abandhavakrita, Abandhukrita, Abhikirnikrita, Abhimukhikrita, Abhinirvyakrita, Abhinitkrita, Abhisamdhikrita, Abhisamskrita, Abhisatkrita, Abhyalamkrita, Abhyantarikrita, Abhyupakrita, Abrukrita, Adaivakrita, Adhahkrita, Adhanishkrita, Adharikrita, Adhikarmakrita, Adhikrita, Adhyagnikrita.
Full-text (+1983): Kiniya, Kritayuga, Kritakrita, Kritavedin, Krayakrita, Kritanna, Kritavastha, Kritakriya, Akrita, Kritakritya, Anayasakrita, Pancadhiva, Kritay, Kritam, Kritagas, Kritanishcaya, Raudraka, Kritavesha, Kritamukha, Kritapunkha.
Relevant text
Search found 172 books and stories containing Krita, Kṛta, Krīta, Kṛtā, Krta; (plurals include: Kritas, Kṛtas, Krītas, Kṛtās, Krtas). You can also click to the full overview containing English textual excerpts. Below are direct links for the most relevant articles:
Garga Samhita (English) (by Danavir Goswami)
Verse 6.15.24 < [Chapter 15 - The Glories of Nṛga-kūpa and Gopī-bhūmi]
Verse 6.15.30 < [Chapter 15 - The Glories of Nṛga-kūpa and Gopī-bhūmi]
Verse 1.9.17 < [Chapter 9 - Description of Vasudeva’s Wedding]
Sahitya-kaumudi by Baladeva Vidyabhushana (by Gaurapada Dāsa)
Text 7.96 < [Chapter 7 - Literary Faults]
Text 7.97 < [Chapter 7 - Literary Faults]
Text 7.109 < [Chapter 7 - Literary Faults]
Rig Veda (translation and commentary) (by H. H. Wilson)
Manusmriti with the Commentary of Medhatithi (by Ganganatha Jha)
Verse 9.159-160 < [Section XXII - The Relative Status of the Twelve Kinds of Sons]
Verse 1.70 < [Section XL - The ‘day’ of Brahmā and the ‘Yugas’]
Verse 9.302 < [Section XL - Personal Behaviour of the King]
The Tattvasangraha [with commentary] (by Ganganatha Jha)
Verse 391 < [Chapter 8 - Examination of the Doctrine of the Permanence of Things]
Verse 221 < [Chapter 7 - Doctrine of the Self (ātman, ‘soul’)]
Verse 2716-2717 < [Chapter 24b - Arguments against the reliability of the Veda (the Revealed Word)]
Shrimad Bhagavad-gita (by Narayana Gosvami)
Verse 6.41 < [Chapter 6 - Dhyāna-yoga (Yoga through the Path of Meditation)]
Verse 4.15 < [Chapter 4 - Jñāna-Yoga (Yoga through Transcendental Knowledge)]
Verses 1.37-38 < [Chapter 1 - Sainya-Darśana (Observing the Armies)]