Pancabuddha, Pañcabuddha, Pancan-buddha: 2 definitions
Introduction:
Pancabuddha means something in Buddhism, Pali. If you want to know the exact meaning, history, etymology or English translation of this term then check out the descriptions on this page. Add your comment or reference to a book if you want to contribute to this summary article.
Alternative spellings of this word include Panchabuddha.
Images (photo gallery)
In Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (Vajrayana or tantric Buddhism)
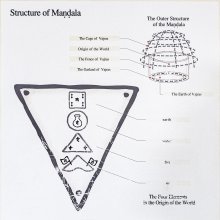
Source: OSU Press: Cakrasamvara SamadhiPañcabuddha (पञ्चबुद्ध) refers to the “five Buddhas”, according to the Guru Mandala Worship (maṇḍalārcana) ritual often performed in combination with the Cakrasaṃvara Samādhi, which refers to the primary pūjā and sādhanā practice of Newah Mahāyāna-Vajrayāna Buddhists in Nepal.—Accordingly, “Homage to the Pañca Buddha’s (pañcabuddha—namas te pañca-buddhānāṃ) skull bone Buddha relics, In the middle Vairocana Buddha, Pañca Buddha, I give homage”.

Tibetan Buddhism includes schools such as Nyingma, Kadampa, Kagyu and Gelug. Their primary canon of literature is divided in two broad categories: The Kangyur, which consists of Buddha’s words, and the Tengyur, which includes commentaries from various sources. Esotericism and tantra techniques (vajrayāna) are collected indepently.
General definition (in Buddhism)
Source: Wisdom Library: Dharma-samgrahaPañcabuddha (पञ्चबुद्ध) refers to the “five Buddhas” or “five Tathagatas” as defined in the Dharma-saṃgraha (section 3):
- Vairocana (Shining Buddha),
- Akṣobhya (Immovable Buddha),
- Ratnasambhava (Jewel-Born Buddha),
- Amitābha (Endless-Light Buddha),
- Amoghasiddhi (Unfailing Buddha).
The Dharma-samgraha (Dharmasangraha) is an extensive glossary of Buddhist technical terms in Sanskrit (e.g., pañcabuddha). The work is attributed to Nagarguna who lived around the 2nd century A.D.
See also (Relevant definitions)
Partial matches: Buddha, Panca.
Full-text (+9): Pancananan, Akshobhya, Amoghasiddhi, Jinadhatu, Vairocananatha, Vairocana, Amitabha, Ratnasambhava, Five Tathagatas, Five Buddhas, Five Dhyani Buddhas, Unfailing Buddha, Prajnadevi, Endless-Light Buddha, Pancavarna, Pancatara, Shining Buddha, Immovable Buddha, Jewel-Born Buddha, Ashvasana.
Relevant text
No search results for Pancabuddha, Pañcabuddha, Pañca-buddha, Pancan-buddha, Panca-buddha, Pañcan-buddha; (plurals include: Pancabuddhas, Pañcabuddhas, buddhas) in any book or story.