Glass: 1 definition
Introduction:
Glass means something in Hinduism, Sanskrit. If you want to know the exact meaning, history, etymology or English translation of this term then check out the descriptions on this page. Add your comment or reference to a book if you want to contribute to this summary article.
Images (photo gallery)
In Hinduism
Ayurveda (science of life)
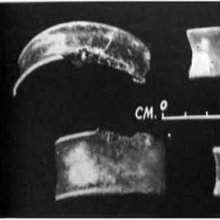
Source: Advances in Zoology and Botany: Indigenous Knowledge of Some Medicinal Plants of Himalaya RegionGlass refers to the medicinal plant “Prunus avium L.” from the Rosaceace family, and is used for ethnomedicine treatment of Fever in Ahmednagar district, India. The parts used are: “Wood, Fruit, Leaves”. Instructions for using the plant named Glass: Leaves are used as fodder. Wood is used as fuel.

Āyurveda (आयुर्वेद, ayurveda) is a branch of Indian science dealing with medicine, herbalism, taxology, anatomy, surgery, alchemy and related topics. Traditional practice of Āyurveda in ancient India dates back to at least the first millenium BC. Literature is commonly written in Sanskrit using various poetic metres.
See also (Relevant definitions)
Starts with: Glasswort.
Full-text (+522): Kaca, Darpaṇa, Kacakupi, Jalataranga, Kacaka, Khatakhadaka, Kacabhajana, Mukura, Cashaka, Bhinga, Aina, Cashma, Acushana, Kacara, Kacamani, Bilora, Valukayantra, Kacavakayantra, Kacaghati, Arashi.
Relevant text
Search found 156 books and stories containing Glass; (plurals include: Glasses). You can also click to the full overview containing English textual excerpts. Below are direct links for the most relevant articles:
Parables of Rama (by Swami Rama Tirtha)
Story 73 - Infinity < [Chapter X - Maya]
Story 26 - How the Infinite can be perceived < [Chapter IV - God-consciousness]
Story 84 - Two ways of Acquiring Knowledge < [Chapter XI - Mind]
Settlement in Early Historic Ganga Plain (by Chirantani Das)
Part 5 - Glass industry of the Vārāṇasī region < [Chapter VI - Vārāṇasī: Emergence of the Urban Centre and Seat of Administration]
Part 4 - Agriculture in the NBPW phase < [Chapter I - The Case Study of Rājagṛha]
Part 5 - Minerals located near the Vārāṇasī region < [Chapter V - Rise of Vārāṇasī as a Nodal Centre]
Amarakoshodghatana of Kshirasvamin (study) (by A. Yamuna Devi)
Daily Life (4): Household Articles < [Chapter 3 - Social Aspects]
Economics (3): Goods of trade < [Chapter 3 - Social Aspects]
A Discourse on Paticcasamuppada (by Venerable Mahasi Sayadaw)
Bifurcated Love < [January – March, 1994]
The Stranger in The Tent < [January – March, 1981]
Letters from the West < [January-February, 1929]
Harshacharita (socio-cultural Study) (by Mrs. Nandita Sarmah)
5.1. Food and Drinks < [Chapter 6 - Other Socio-Cultural Aspects]
1. Similarities (5): Economic Condition < [Chapter 8 - Comparative Society as described in the Kādambarī and the Harṣacarita]
4. Economic Condition < [Chapter 6 - Other Socio-Cultural Aspects]
Related products
(+13 more products available)