Ganita, Gaṇita: 22 definitions
Introduction:
Ganita means something in Hinduism, Sanskrit, Buddhism, Pali, Marathi, Hindi. If you want to know the exact meaning, history, etymology or English translation of this term then check out the descriptions on this page. Add your comment or reference to a book if you want to contribute to this summary article.
Alternative spellings of this word include Ganit.
In Hinduism
Purana and Itihasa (epic history)
Source: archive.org: Puranic EncyclopediaGaṇita (गणित).—A Viśvadeva, who used to calculate the course of time and ages. (Anuśāsana Parva, Chapter 91, Verse 36).
Source: Cologne Digital Sanskrit Dictionaries: The Purana IndexGaṇita (गणित).—The science of computation (Algebra, Geometry and Arithmetic).*
- * Vāyu-purāṇa 70. 15.

The Purana (पुराण, purāṇas) refers to Sanskrit literature preserving ancient India’s vast cultural history, including historical legends, religious ceremonies, various arts and sciences. The eighteen mahapuranas total over 400,000 shlokas (metrical couplets) and date to at least several centuries BCE.
Jyotisha (astronomy and astrology)
Source: Wisdom Library: Brihat Samhita by VarahamihiraGaṇita (गणित) refers to “astronomy”, according to the Bṛhatsaṃhitā (chapter 2), an encyclopedic Sanskrit work written by Varāhamihira mainly focusing on the science of ancient Indian astronomy astronomy (Jyotiṣa).—Accordingly, “That prince meets with ruin who does not support a Jyotiṣaka well-versed in all the Divisions and Subdivisions of Saṃhitā and in Horoscopy and Astronomy [i.e., gaṇita]. Even men who, having conquered their passions and cut asunder all ties of family, live in woods, desire to question a learned Jyotiṣaka regarding their future”.
Source: Wikibooks (hi): Sanskrit Technical TermsGaṇita (गणित).—1. Computation, calculation; mathematics in general. 2. The mathematical component of astronomy and astrology. Note: Gaṇita is a Sanskrit technical term used in ancient Indian sciences such as Astronomy, Mathematics and Geometry.

Jyotisha (ज्योतिष, jyotiṣa or jyotish) refers to ‘astronomy’ or “Vedic astrology” and represents the fifth of the six Vedangas (additional sciences to be studied along with the Vedas). Jyotisha concerns itself with the study and prediction of the movements of celestial bodies, in order to calculate the auspicious time for rituals and ceremonies.
Ganitashastra (Mathematics and Algebra)
Source: Wisdom Library: Brihat Samhita (Mathematics)Gaṇita (गणित) refers to “mathematicians”, according to the Bṛhatsaṃhitā (chapter 15) (“On the nakṣatras—‘asterisms’”), an encyclopedic Sanskrit work written by Varāhamihira mainly focusing on the science of ancient Indian astronomy astronomy (Jyotiṣa).—Accordingly, “Those who are born on the lunar day of Citrā will be dealers in jewels, precious stones, fine cloths, writers and singers, manufacturers of perfumes, good mathematicians (gaṇita-paṭu), weavers, surgeons, oculists and dealers in Rājadhānya. [...]”.
Source: archive.org: Hindu MathematicsGaṇita (गणित) refers to the “science of calculation” or “measurement and calculation”.—The term gaṇita is a very ancient one and occurs copiously in Vedic literature. The Vedāṅga-jyotiṣa (c. 1200 B.C.) gives it the highest place of honour among the sciences which form the Vedāṅga: “As the crests on the heads of peacocks, as the gems on the hoods of snakes, so is gaṇita at the top of the sciences known as the Vedāṅga”.
The subjects treated in the Hindu gaṇita of the early renaissance period consisted of the following:
- parikarma (“fundamental operations”),
- vyavahāra (“determinations”),
- rajju (“rope,” meaning geometry),
- rāśi (“rule of three”),
- kalāsavarṇa (“operations with fractions”),
- yāvattāvat (“as many as,” meaning simple equations),
- varga (“Square,” meaning quadratic equations),
- ghana (“Cube”, meaning cubic equations),
- vargavarga (biquadratic equations) and
- vikalpa (“permutations and combinations”).
Praise of Gaṇita (calculation) as found in the according to Mahāvīra in the Gaṇitasārasaṃgraha: “In all transactions which relate to worldly, Vedic or other similar religious affairs calculation is of use. In the science of love, in the science of wealth, in music and in drama, in the art of cooking, in medicine,, in architecture, in prosody, in poetics and poetry, in logic and grammar and such other things, and in relation to all that constitutes the peculiar value of the arts, the science of calculation (gaṇita) is held in high esteem. [...] The number, the diameter and the perimeter of islands, oceans and mountains; the extensive dimensions of the rows of habitations and halls belonging to the inhabitants of the world, of the interspace between the worlds, of the world of light, of the world of the gods and of the dwellers in hell, and other miscellaneous measurements of all sorts—all these are made out by the help of gaṇita. [...] The configuration of living beings therein, the length of their lives, their eight attributes, and other similar things; their progress and other such things, their staying together, etc.—all these are dependent upon gaṇita (for their due comprehension). [...] What is the good of saying much? Whatever there is in all the three worlds, which are possessed of moving and non-moving beings, cannot exist as apart from gaṇita (measurement and calculation)”.
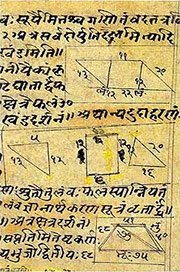
Ganitashastra (शिल्पशास्त्र, gaṇitaśāstra) refers to the ancient Indian science of mathematics, algebra, number theory, arithmetic, etc. Closely allied with astronomy, both were commonly taught and studied in universities, even since the 1st millennium BCE. Ganita-shastra also includes ritualistic math-books such as the Shulba-sutras.
Yoga (school of philosophy)
Source: ORA: Amanaska (king of all yogas): A Critical Edition and Annotated Translation by Jason BirchGaṇita (गणित) refers to the “(doctrines of) mathematics”, according to the Amanaska Yoga treatise dealing with meditation, absorption, yogic powers and liberation.—Accordingly, as Īśvara says to Vāmadeva: “[...] Not by studying the doctrines of scriptural exegesis, logic, planets and mathematics (gaṇita), nor by the Vedas, Upaniṣads, Dharmaśāstras [and the like]; not even by lexicons nor metre, grammar, poetry nor rhetoric; the sage's attainment of the highest reality is gained only from the oral teachings of his own guru.[...]”.

Yoga is originally considered a branch of Hindu philosophy (astika), but both ancient and modern Yoga combine the physical, mental and spiritual. Yoga teaches various physical techniques also known as āsanas (postures), used for various purposes (eg., meditation, contemplation, relaxation).
Shaktism (Shakta philosophy)
Source: Google Books: ManthanabhairavatantramGaṇita (गणित) refers to “(the method of) measuring (time)”, according to the according to the Kularatnoddyota, one of the earliest Kubjikā Tantras.—Accordingly, while describing Vṛkṣanātha’s entry into the world: “When the Vārāha Aeon and six Manvantaras had passed thus (along with) the Manus and those born from them, then, having fashioned an appropriate body in the middle of the present (age), four Ages (yuga) past in the course of time counting in terms of aeons. (Thus) according to (this) method of measuring (time) (gaṇita-vidhi) twenty-eight Ages (passed) up to the end of the Dvāpara age”.

Shakta (शाक्त, śākta) or Shaktism (śāktism) represents a tradition of Hinduism where the Goddess (Devi) is revered and worshipped. Shakta literature includes a range of scriptures, including various Agamas and Tantras, although its roots may be traced back to the Vedas.
Languages of India and abroad
Pali-English dictionary
Source: BuddhaSasana: Concise Pali-English Dictionarygaṇita : (pp. of gaṇeti) counted. (nt.), arithmetic.

Pali is the language of the Tipiṭaka, which is the sacred canon of Theravāda Buddhism and contains much of the Buddha’s speech. Closeley related to Sanskrit, both languages are used interchangeably between religions.
Marathi-English dictionary
Source: DDSA: The Molesworth Marathi and English Dictionarygaṇita (गणित).—n (S) Calculating, computing, arithmetical operations. 2 The science of computation, comprising arithmetic, algebra, and geometry; distinguished as pāṭīgaṇita, bījagaṇita, rēkhāgaṇita. 3 The sum of a series.
--- OR ---
gaṇita (गणित).—p S Counted, computed, reckoned.
--- OR ---
gaṇita (गणित).—prep By, to &c. each severally, per. Ex. vṛkṣāgaṇīka, khiḍakīgaṇīka, gṛhāgaṇīka, khēpēgaṇīka.
--- OR ---
gaṇīta (गणीत).—prep By, to &c. each severally, per. Ex. vṛkṣāgaṇīka, khiḍakīgaṇīka, gṛhāgaṇīka, khēpēgaṇīka.
Source: DDSA: The Aryabhusan school dictionary, Marathi-Englishgaṇita (गणित).—n Calculating or computing. The science of computation mathe- matics. p Counted.
--- OR ---
gaṇita (गणित).—prep By, to, &c., each severally, per.
Marathi is an Indo-European language having over 70 million native speakers people in (predominantly) Maharashtra India. Marathi, like many other Indo-Aryan languages, evolved from early forms of Prakrit, which itself is a subset of Sanskrit, one of the most ancient languages of the world.
Sanskrit dictionary
Source: DDSA: The practical Sanskrit-English dictionaryGaṇita (गणित).—p. p. [gaṇ-kta]
1) Counted, numbered, calculated.
2) Regarded, cared for &c; see गण् (gaṇ).
Source: Cologne Digital Sanskrit Dictionaries: Shabda-Sagara Sanskrit-English DictionaryGaṇita (गणित).—mfn.
(-taḥ-tā-taṃ) Numbered, counted, reckoned, calculated. n.
(-taṃ) 1. The science of computation, comprising arithmetic, algebra, and geometry, distinguished as pāṭīgaṇitaṃ, vījagaṇitaṃ and rekhāgaṇitaṃ. 2. Calculating, numbering. E. gaṇa to count, affix kta.
Source: Cologne Digital Sanskrit Dictionaries: Cappeller Sanskrit-English DictionaryGaṇita (गणित).—[adjective] numbered, reckoned, valued at ([instrumental]); [neuter] reckoning, calculation.
Source: Cologne Digital Sanskrit Dictionaries: Monier-Williams Sanskrit-English Dictionary1) Gaṇita (गणित):—[from gaṇ] mfn. counted, numbered, reckoned, calculated, [Mahābhārata; Bhāgavata-purāṇa; Vetāla-pañcaviṃśatikā]
2) [v.s. ...] n. reckoning, calculating, science of computation (comprising arithmetic, algebra, and geometry, pāṭīor vyakta-, bīja-, & rekhā-), [Mahābhārata i, 293; Mṛcchakaṭikā i, 4; Varāha-mihira’s Bṛhat-saṃhitā] etc.
3) [v.s. ...] the astronomical or astrological part of a Jyotiḥśāstra (with the exception of the portion treating of nativities), [Varāha-mihira’s Bṛhat-saṃhitā]
4) [v.s. ...] the sum of a progression
5) [v.s. ...] sum (in general).
6) Gaṇitā (गणिता):—[from gaṇ] f. of ta q.v.
Source: Cologne Digital Sanskrit Dictionaries: Yates Sanskrit-English DictionaryGaṇita (गणित):—[(taḥ-tā-taṃ) a.] Numbered. n. Science of counting; counting.
Source: DDSA: Paia-sadda-mahannavo; a comprehensive Prakrit Hindi dictionary (S)Gaṇita (गणित) in the Sanskrit language is related to the Prakrit words: Gaṇāvia, Gaṇiya.
[Sanskrit to German]
Sanskrit, also spelled संस्कृतम् (saṃskṛtam), is an ancient language of India commonly seen as the grandmother of the Indo-European language family (even English!). Closely allied with Prakrit and Pali, Sanskrit is more exhaustive in both grammar and terms and has the most extensive collection of literature in the world, greatly surpassing its sister-languages Greek and Latin.
Hindi dictionary
Source: DDSA: A practical Hindi-English dictionaryGaṇita (गणित) [Also spelled ganit]:—(nm) Mathematics; ~[jña] a mathematician; —[vidyā] mathematical science; [gaṇitīya] mathematical; •[sāṃkhyikī] mathematical Statistics.
...
Kannada-English dictionary
Source: Alar: Kannada-English corpusGaṇita (ಗಣಿತ):—[adjective] counted; numbered; enumerated; reckoned with.
--- OR ---
Gaṇita (ಗಣಿತ):—
1) [noun] the act of counting, reckoning, etc.
2) [noun] the abstract science of number, quantity, and space studied in its own right or as applied to other disciplines such as physics, engineering, etc.; mathematics.
3) [noun] ಗಣಿತಮಾಡು [ganitamadu] gaṇita māḍu to count; to calculate; to enumerate; ಗಣಿತಹಾಕು [ganitahaku] gaṇita hāku = ಗಣಿತಮಾಡು [ganitamadu].
Kannada is a Dravidian language (as opposed to the Indo-European language family) mainly spoken in the southwestern region of India.
Nepali dictionary
Source: unoes: Nepali-English DictionaryGaṇita (गणित):—n. mathematics; adj. counted; calculated;
Nepali is the primary language of the Nepalese people counting almost 20 million native speakers. The country of Nepal is situated in the Himalaya mountain range to the north of India.
See also (Relevant definitions)
Starts with (+29): Ganitabhushana, Ganitacandrika, Ganitacudamani, Ganitadanda, Ganitadevitirtha, Ganitadhyaya, Ganitadivasaka, Ganitagata, Ganitagranthavishesha, Ganitajna, Ganitakalpadruma, Ganitakaumudi, Ganitakoshtaka, Ganitalata, Ganitamalati, Ganitamanjari, Ganitamrita, Ganitamritakupika, Ganitamritalahari, Ganitamritasagari.
Ends with (+30): Adhiganita, Aganita, Aksharamkaganita, Ankaganita, Anuganita, Apariganita, Apurnankaganita, Avaganita, Avyaktaganita, Ayanacayanadiganita, Balaganita, Bhadraganita, Bijaganita, Brahmatulyaganita, Dashavidhaganita, Dinaganita, Drigganita, Goleganita, Grahaganita, Horaganita.
Full-text (+511): Ganiya, Pariganita, Patiganita, Vijaganita, Suvarnaganita, Trairashika, Aganita, Viganita, Ganitadevitirtha, Grahaganita, Bhadraganita, Vyakta, Avkalan, Ganay, Bijaganita, Ganitalata, Ganitapancavimshatika, Ganitamalati, Anavartin, Aganitalajja.
Relevant text
Search found 14 books and stories containing Ganita, Gaṇīta, Gaṇita, Gaṇitā; (plurals include: Ganitas, Gaṇītas, Gaṇitas, Gaṇitās). You can also click to the full overview containing English textual excerpts. Below are direct links for the most relevant articles:
Puranic encyclopaedia (by Vettam Mani)
Karmic Astrology—a Study (by Sunita Anant Chavan)
Part 2.2.5 - Peculiarities of Gaṇita (calculations) < [Chapter 2 - Jyotiḥśāstra and the Concept of Karman]
Part 2.2.1 - Gaṇita of the Veda and Vedāṅga Period (Introduction) < [Chapter 2 - Jyotiḥśāstra and the Concept of Karman]
Part 2.2.6 - Gaṇita of the Siddhānta Period < [Chapter 2 - Jyotiḥśāstra and the Concept of Karman]
Significance of the Moon in Ancient Civilizations (by Radhakrishnan. P)
2. Upanishad Shantimatra and Result of Karma < [Chapter 4 - Contemporary Astrological Viewpoint and Moon]
8. Contributions of Varahamihira < [Chapter 2 - A Sceintific Outlook on Astrology]
15. Findings Of The Thesis < [Chapter 15 - Conclusion]
Sahitya-kaumudi by Baladeva Vidyabhushana (by Gaurapada Dāsa)
Text 4.96 < [Chapter 4 - First-rate Poetry]
Philosophy of Charaka-samhita (by Asokan. G)
General attributes (sāmānya-guṇas) < [Chapter 2 - Fundamental Categories]
Vastu-shastra (1): Canons of Architecture (by D. N. Shukla)
(i) Scope of Architecture (Vāstu) < [Chapter 2 - Scope and Subject-matter]
(v) The character of the building aspect etc. (Patākādi-ṣaṭ-chandas) < [Chapter 6 - Fundamental Canons of Hindu Architecture]
(ii) The Site-planning (Vāstupada-vīnyāsa) < [Chapter 6 - Fundamental Canons of Hindu Architecture]
Related products

